Any living organism requires sugar and oxygen to survive. The food that we consume contains carbohydrates, fats and proteins as nutrients. Our body requires energy to function. This energy is derived from the carbohydrates in the food. When the food is consumed all the sugar in the food is absorbed by the intestines and put into the blood. In the blood the sugar is converted into tryglecerides and stored in the form of fat in the body. When the body requires energy these tryglecerides get converted into sugar again and is burnt in the cells of the body. Whatever is the amount of sugar that you consume, it should not stay in your blood if the body is functioning properly. The sugar levels in the blood in the state of fasting should be less than 110 mg/dl and the levels should be less than 140 mg/dl two hours after consuming a meal. If the sugar levels are higher than this then it means that the body's mechanism of converting sugar into fat is working properly and the person is deemed to have diabetes.
|
|

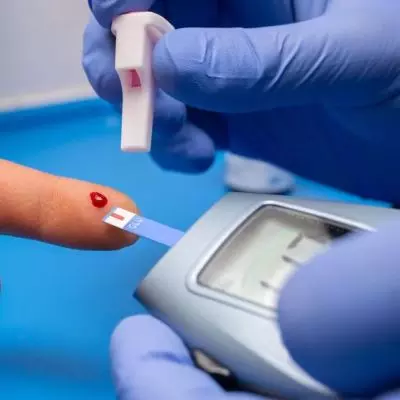
Blood Sugar is tested in several ways. Fasting blood sugar is done with 12 hours of fasting. Only water intake is allowed during these 12 hours of fasting. Smoking is also prohibited to get an accurate value. The blood sample is taken from the vein or through a prick on the finger and the drop of blood is placed on a chemical strip which is inserted into a glucometer which gives the value of sugar in the blood.
When you take a meal, the food goes into the abdomen and then into the intestine. The sugar in the food is absorbed by the intestine and put into the blood. This process takes two hours. Post Prandial blood sugar test is done 2 hours after taking a meal with atleast 75 gms of carbohydrates. This is supposed to be the highest sugar levels in your body at any time of the day. After 2 hours the sugar in the blood starts to get converted into fat and the sugar levels would come down.
Random blood sugar is done at any time of the day and the value would be between fasting blood sugar and post prandial blood sugar.
|
|

1 Blood Sugar Fasting 70-110 mg/dl
2 Blood Sugar PP 70-140 mg/dl
3 Blood Sugar Random 70-140 mg/dl
If the blood sugar levels are above 180 mg/dl then the kidneys start to excrete the excess sugar through urine. In this process the kidneys start getting damaged. It is therefore extremely important to keep the blood sugar below 180 at all times. One of the best test to find out whether your blood sugar remains below 180 at all times of the day is to get Glycosylated Hemoglobin (HbA1C) test done. If the value of HbA1C is below 5.7 then your sugar levels are fine at all times of the day.
The best way to keep your sugar levels under good control is to eat as much of natural glucose as possible. Natural Glucose (C6H12O6) is found in plants - fruits and vegetables. If you eat the fruits and vegetables in their natural form i.e. without cooking then your sugar levels would be fine.
Eating cooked food, processed food and artificial sugars result in spike in sugar values and would eventually lead you towards diabetes.
|
|
What is blood sugar test ?
Diabetes is one of the most common problem in India. India has already become the “Diabetes Capital of the World” as it has so many diabetic patients. The Blood Sugar test is done to find out the sugar levels in the blood. This is done in three ways, Fasting Blood Sugar(FBS), Random Blood Sugar (RBS) and Postprandial Blood Sugar (Blood Sugar PP). Fasting blood sugar is done with overnight fasting. Random blood sugar can be done anytime and postprandial blood sugar is generally done along with Fasting blood sugar. In postprandial blood sugar or Blood Sugar PP as commonly called person is given 75gms of glucose to consume and after 2 hours of consumption the test is done.
Why should I do the Blood Sugar Test ?
Blood Glucose test is part of the health checkup packages at Maurya Labs in Purnea, Bihar. Ideally every person should get the health check done once a year. However, if you have family history of diabetes or your are obese, then you need to keep your sugar levels in check and get the blood sugar levels tested at least once every 3 months along with HbA1c which gives the average of 3 months of blood sugar levels.
How is the Blood Sugar Test Done ?
Blood Sugar test is done using the sample drawn from the vein by a phlebotomist at home or at centre and then testing is done on analyzer. People who are already diagnosed with type 2 diabetes can test at home using a device called glucometer. However, the test done on analyzers are considered more authentic.
How often Blood Sugar Test be Done ?
A non-diabetic person should get the test done as a part of annual health check package. People who are non diabetic but have family history of diabetes should get it done every 3 months along with HbA1c. Diabetic people should keep testing everyday or as per the direction from the treating physician.



| Most Important Test in any Disease | |
| 22 Parameters Covered | |
| No Preparation Required | |
| Done on 6 Part Hemoanalyzer - First in Seemanchal | |
| Read More |
|
|
| Most Important Test in Women | |
| 3 Parameters – T3, T4,TSH | |
| No Preparation Required | |
| Done on Fully Automatic Thyroid Analyzer Centaur CP from USA | |
| Read More |
|
|
| Most Important Test for Diabetics | |
| Gives average sugar over 3 months | |
| No Preparation Required | |
| Done on Glycohemoglobin Analyzer, Bio Rad from USA |
|
| Read More |
|
|
| Most Popular Health Checkup for Sugar and High BP patients |
|
| 75 Parameters Covered | |
| 12 Hours Fasting Required | |
| Total Cost Rs. 8210 Discount Rs. 4210 | |
| Read More |
|
|
| Full Body Checkup in Men aged less than 50 Years |
|
| 125 Parameters Covered | |
| 12 Hours Fasting Required | |
| Total Cost Rs 10710 Discount Rs 5510 | |
| Read More |
|
|
| Full Body Checkup in Women aged less than 50 Years |
|
| 130 Parameters Covered | |
| 12 Hours Fasting Required | |
| Total Cost Rs 12710 Discount Rs 6510 | |
| Read More |
|
|
Know Your Blood Count

Checking Organ Health

Hormonal Balance

Infections in the Body



